Picor, a tool to find, from a reference image, the closest image in a collection
This tool allows experimenting with different methods to identify, from a given image, the closest image in a collection. It is suitable for working with image collections where there are many similar images.

The specific use case studied in this project is, starting from an image taken from a video, being able to find the exact matching image in the video, knowing that the target image may have differences in:
- encoding,
- resolution,
- quality,
- colorimetry.
The source code as well as installation and usage instructions are available on the project's GitHub page.
Methods Used
Currently, two methods are available in the tool:
- cross-correlation
- average hash
In all cases, the image is preprocessed:
- resized to 32x32 pixels,
- converted to grayscale.
Cross-correlation
It is expressed as follows:
where:
ris the correlation result,xandyare two grayscale images to compare,iis the pixel index in the images.
The closer r is to 1, the more similar the images are.
The C code implementation is in lib/xcorr.c file.
Average hash
This method consists of taking the grayscale pixel vector of the image and computing the mean value. Then, for each pixel greater than or equal to the mean, a binary 1 is added to the hash, and for each pixel lower than the mean, a binary 0 is added.
To compare two images, a distance must be computed between their hashes. The smaller the distance, the more similar the images are.
The C code implementation is in lib/avghash.c file.
Results
Both methods provide very similar results. However, using average hash allows pre-indexing the image collection, making it possible to perform searches later.
Below is an example result. The Blender Studio animated film Elephants Dream was used. The image collection is in JPG format, resolution 1920x1080. The search image is also in JPG format, resolution 434x244, and of poor quality.
The processing time for the input images (in JPG) is not included in the displayed durations.
This is an example output from picor-basic-pic-retriever-stats. It was run with 551 images on an Intel(R) Core(TM) i7-7500U CPU @ 2.70GHz laptop from 2017.

Average hash
Hash computation done in 0.001447s, comparison in 0.000042s.
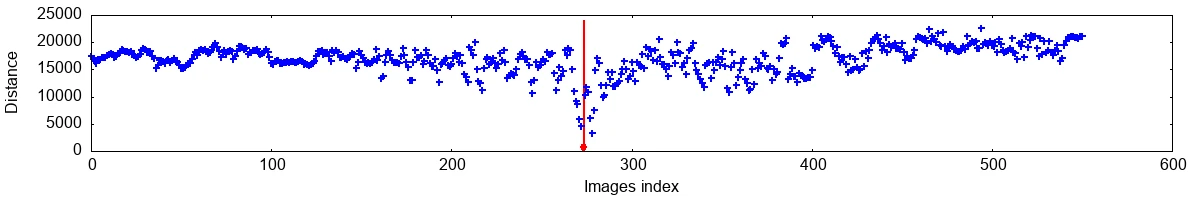
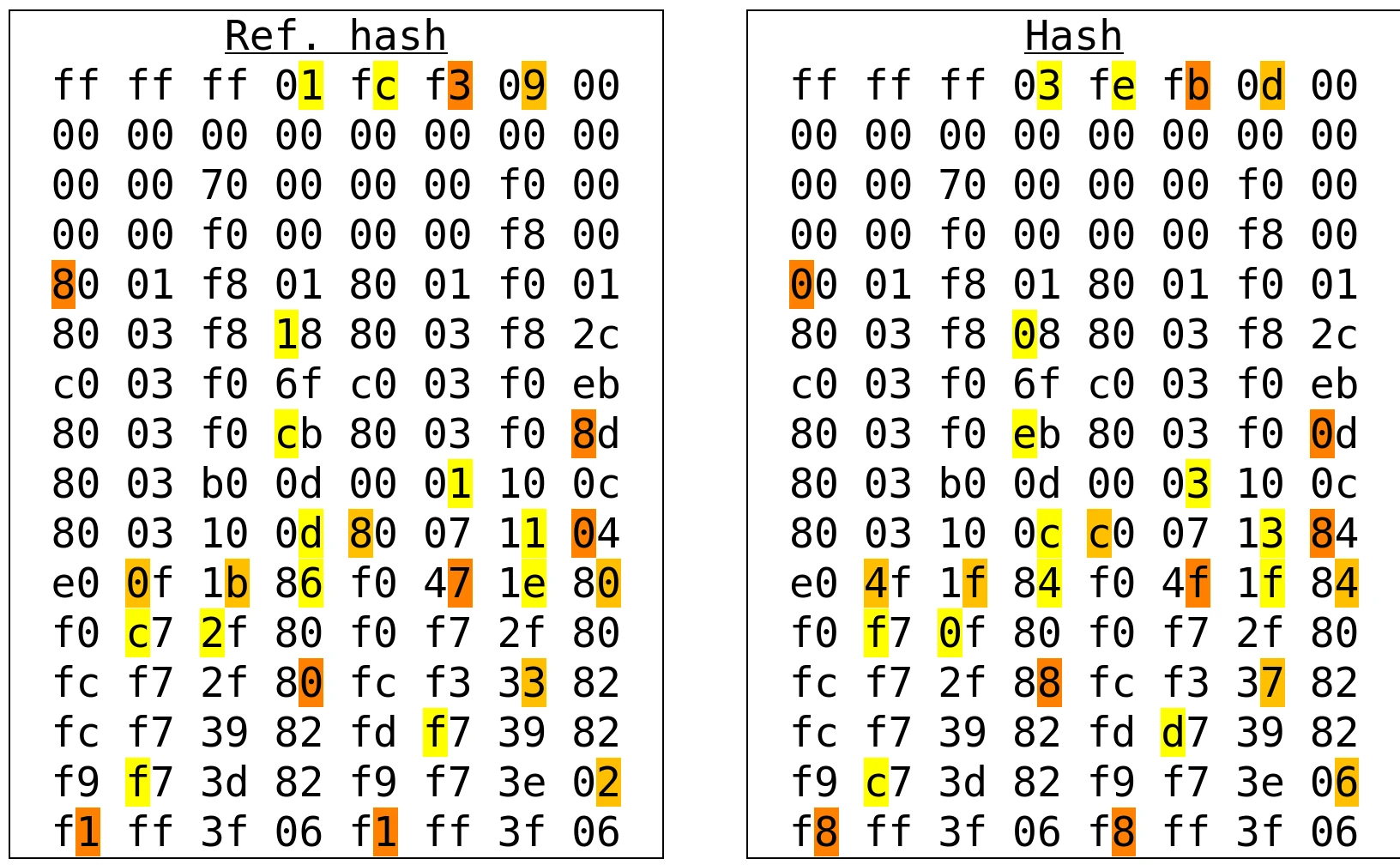
Full result - You can use the left ⬅️ and right ➡️ arrow keys to navigate through the collection, and backspace ⌫ to return to the best-found image.
Cross-correlation
Cross-correlation performed in 0.001465s.
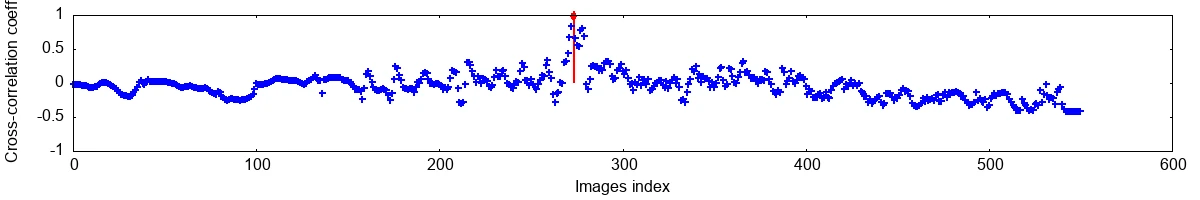
Full result - You can use the left ⬅️ and right ➡️ arrow keys to navigate through the collection, and backspace ⌫ to return to the best-found image.
After several tests on different videos and with various image qualities, it turns out that average hash and cross-correlation are very effective methods for this type of task, both in terms of the accuracy of the retrieved image and the efficiency of resource usage.